Shifting Gears: 5 Additive Manufacturing Solutions for Automotive Manufacturers
While each situation is unique, there are five key ways that AM empowers engineers to solve automotive industry challenges:
1. Customization
The rise of smartphones, autonomous driving features, and the Internet of Things (IoT) have been major contributors to this trend. Not only are consumers seeing cars for their functional use, but also as an extension of their digital lives. As a result, OEMs and car makers are looking outside of traditional manufacturing materials and exploring more recycled plastics and bio-based alternatives.
That’s where additive manufacturing comes in because it moves past the traditional one-size-fits-all method and allows for the customization of parts with ease. This level of specification enables automotive manufacturers to craft parts with complex geometries at a rapid pace.
An example of this in action is Cupra Racing, who leveraged HP’s Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) technology to overcome challenges with car components including side mirrors, brake and water-cooling inlets, and the steering wheel’s center control module. Given the harsh environment that these parts are regularly exposed to, Cupra Racing aimed to produce multiple variants of these components to fine-tune the flexibility and speed of the end-use parts.
Due to MJF’s ability to create strong parts quickly, HP was able to accelerate the design phase and deliver functional parts in just a few days.
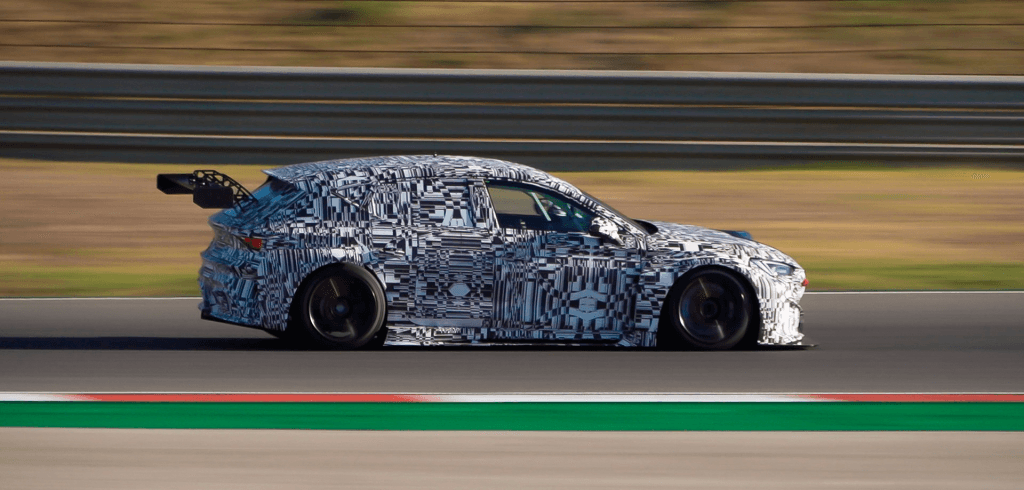

Cupra Racing racecar
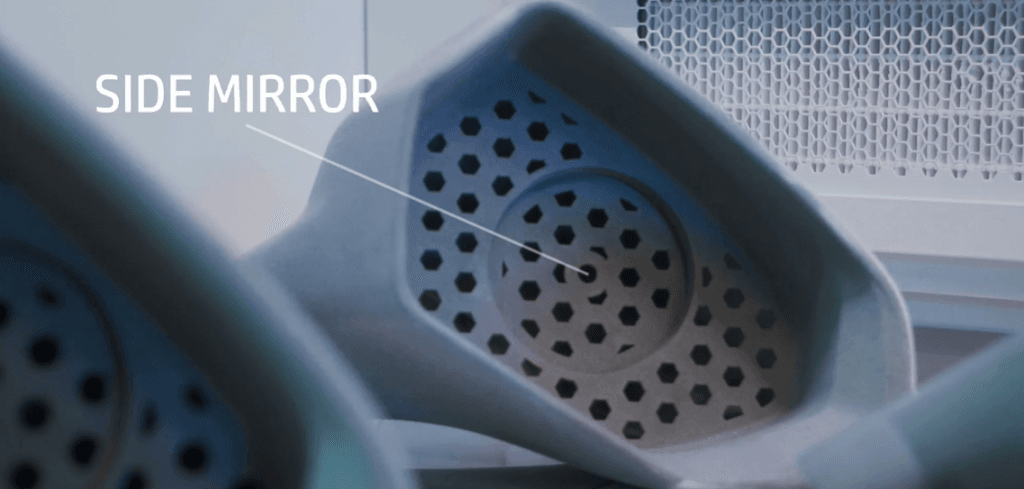
Cupra Racing automotive side mirror created with HP MJF 3D printer
2. Plastics
Let’s look at two common 3D-printed plastic materials that are leading the charge for automotive applications:
Nylon (PA): This strong and flexible thermoplastic is ideal for functional, load-bearing applications such as gears, engine components, and jigs and fixtures. Nylon is known for its ability to withstand high temperatures and chemical resistance.
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS): ABS offers a good balance of strength, rigidity, and heat resistance. Although not as strong as Nylon, it is suitable for prototypes and interior parts such as dashboards and trim panels.
3. Lightweighting
Endeavor 3D’s metal and polymer binder jetting technology eliminate the need for hefty molds and wasteful materials by precisely placing material layer upon layer to maximize output and minimize cost. In doing so, automotive engineers don’t have to sacrifice lightweighting when optimizing the topology of automotive parts.
4. Prototyping
What does this mean for automotive engineers?
To answer it simply, shorter production times. The use of rapid prototyping in 3D printed automotive applications enhances the production process, reducing waiting periods from weeks and months to mere hours and days, thereby improving efficiency. Through this, engineers can test-drive designs and explore complex geometries before committing to costly manufacturing.
In addition, the accelerated design and production phase of the product lifecycle enables automotive manufacturers to bypass expensive tooling, part assembly, and cumbersome post-processing steps.
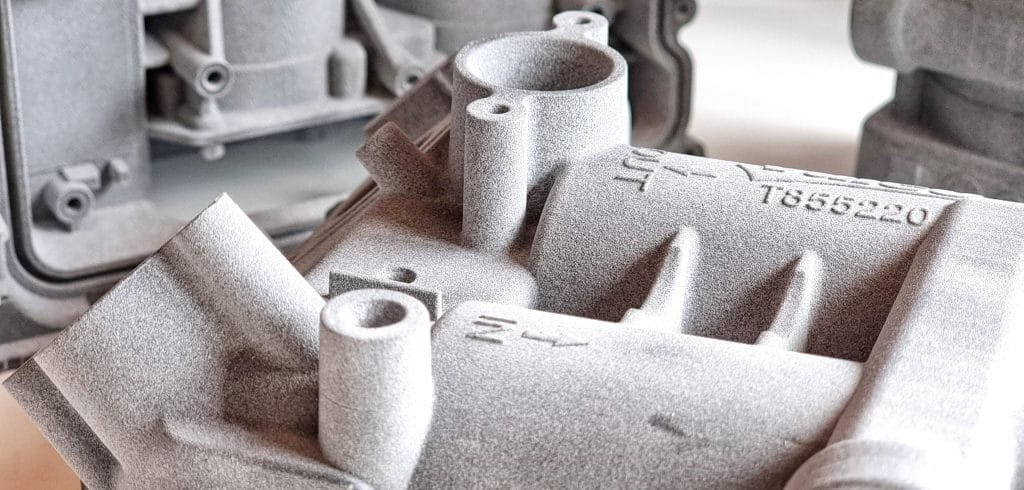

MJF automotive car component
5. A Sustainable Future
Material Waste:
Imagine a manufacturing process where barely any material was wasted but instead reused for subsequent prints. Sounds great, right? That can become a reality with additive manufacturing. It takes a combination of that process with parts that can be produced with exceptional strength and at a lower cost compared to traditional methods.
Additionally, additive manufacturing steps in by building parts layer-by-layer using reusable powders. Subtractive manufacturing such as CNC machining; a process that removes unneeded material by grinding or milling it away, pales in comparison.
Additionally, the precision of digital manufacturing dramatically reduces the material scrap rate by up to 90%, saving automotive manufacturers both time and money. It ultimately eliminates the need for molds and tooling, thus, the requested order size and build volumes are optimized to minimize waste and overproduction.
Supply Chain Efficiency
Digital manufacturing also promotes a more streamlined and sustainable supply chain. Due to the unpredictable nature of automobiles, end-use parts and prototypes must be able to be printed on-demand.
In the past, energy-intensive manufacturing and transportation methods created a supply chain network that required storage for a large volume of parts. Consequently, this meant automotive manufacturers had to predict demand months in advance, substantially reducing the agility of their supply chain.
Additive manufacturing bridges that gap by enabling manufacturers to upload part designs for quickly made iterations seamlessly. This provides the vehicle makers with a virtual warehouse to source for future use. Through and through, 3D printing eliminates the guesswork for demand and its unpredictable nature, costly inventory, and avoidable emissions and creates a more streamlined supply chain process.
The Road Ahead
Additive manufacturing is paving the way forward by leveraging technology and supply chain agility to streamline each stage of the automotive manufacturing process.
From design and engineering to post-processing and fulfillment services, Endeavor 3D is in the driver’s seat when it comes to tackling automakers’ toughest challenges.
Are traditional manufacturing methods holding you back? Contact Us to explore how we can give your automotive designs a competitive edge.