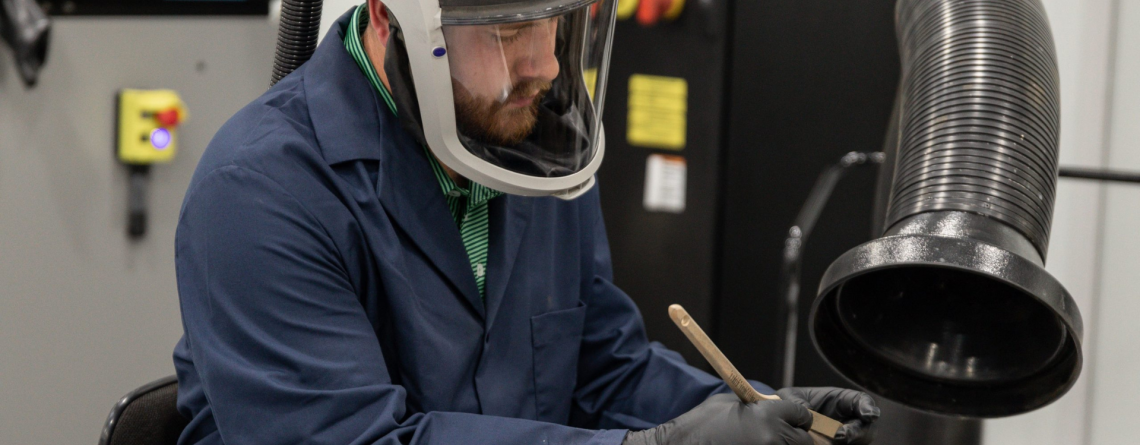
Exploring the Future of Manufacturing: Metal Binder Jetting
What is Metal Binder Jetting?
Metal binder jetting is an additive manufacturing process that involves printing metal parts layer by layer using a binding agent and metal powder. Unlike traditional methods like casting or CNC machining, metal binder jetting can produce highly complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional processes.
In this process, a fine layer of metal powder is spread across a build platform, and a liquid binder is selectively deposited to bond the particles. This process is repeated layer by layer until the part is fully formed. After printing, the part typically undergoes a sintering process, where heat is applied to fuse the metal particles into a solid, fully functional metal part.
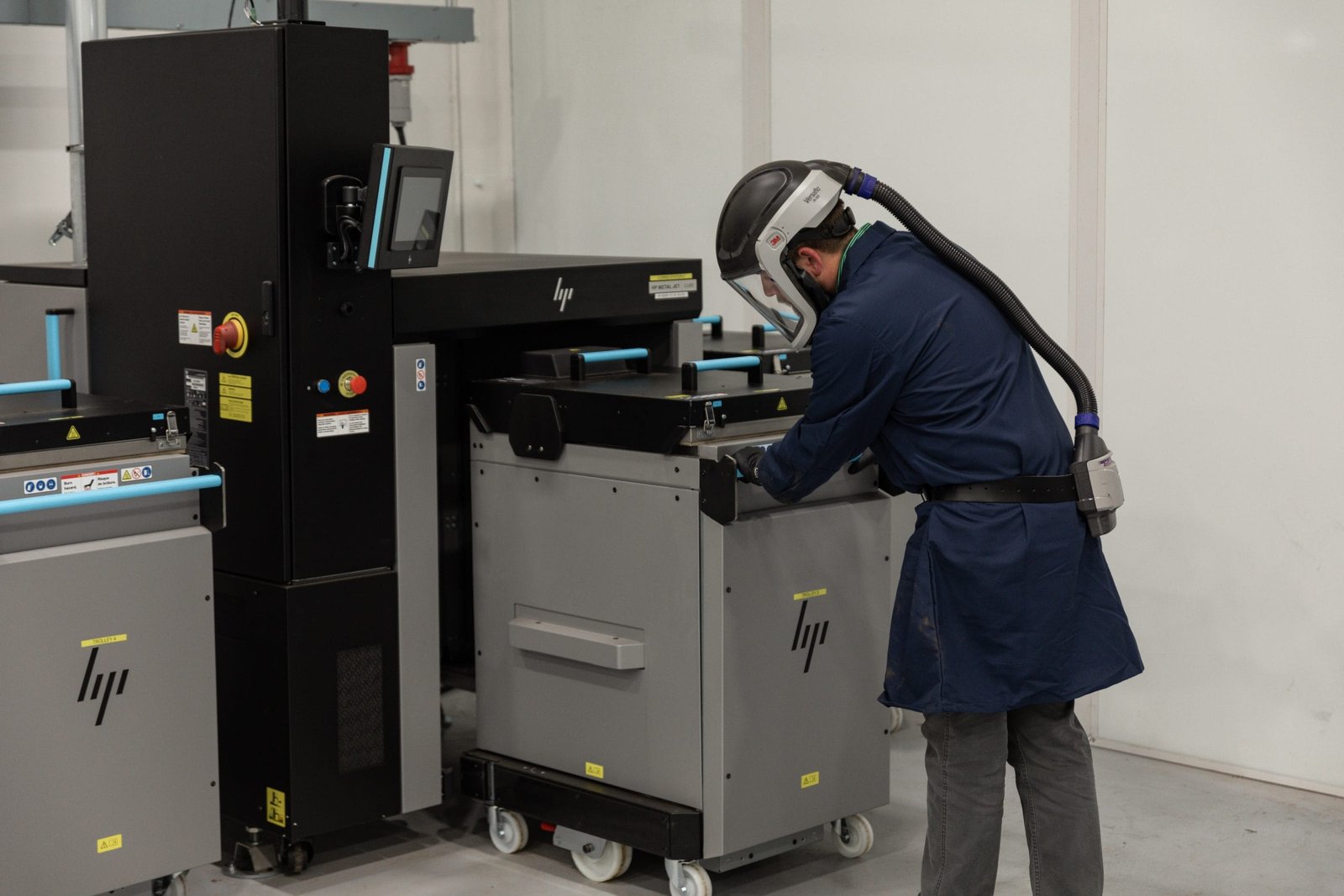

Key Benefits of Metal Binder Jetting
Complex Geometries: Metal binder jetting excels at producing intricate parts with complex geometries that would be time-consuming or costly to produce using traditional methods. This is particularly valuable for industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, where custom, lightweight, and optimized parts are in demand.
Design Freedom: The design flexibility offered by metal binder jetting allows engineers and designers to push the boundaries of what’s possible in product development, leading to lighter, more efficient, and innovative designs.
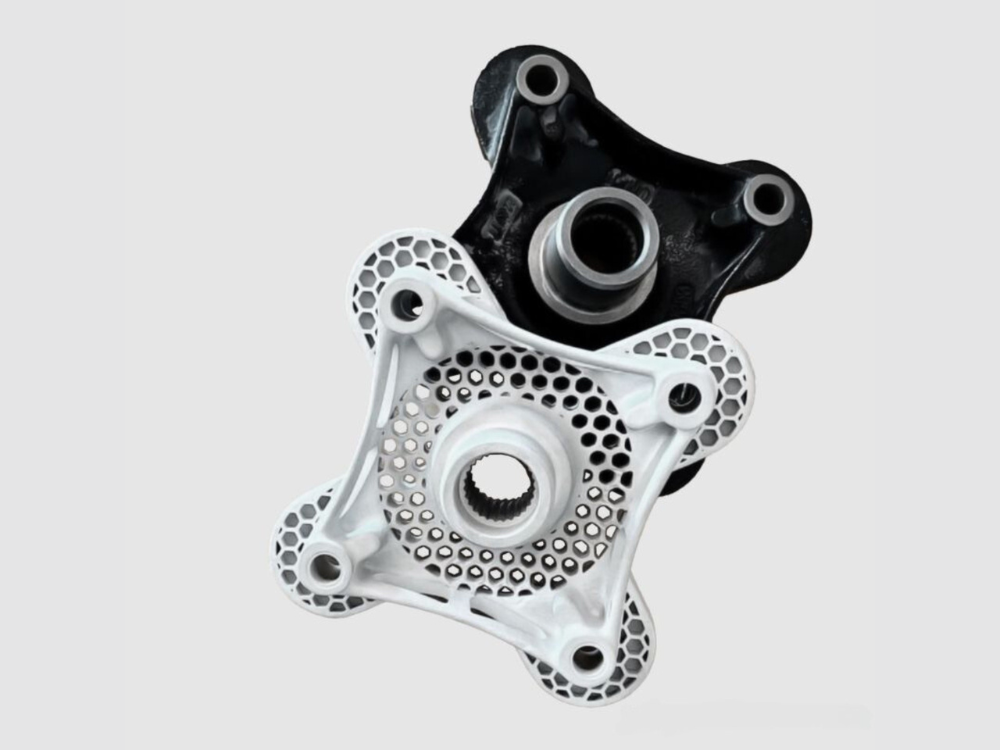

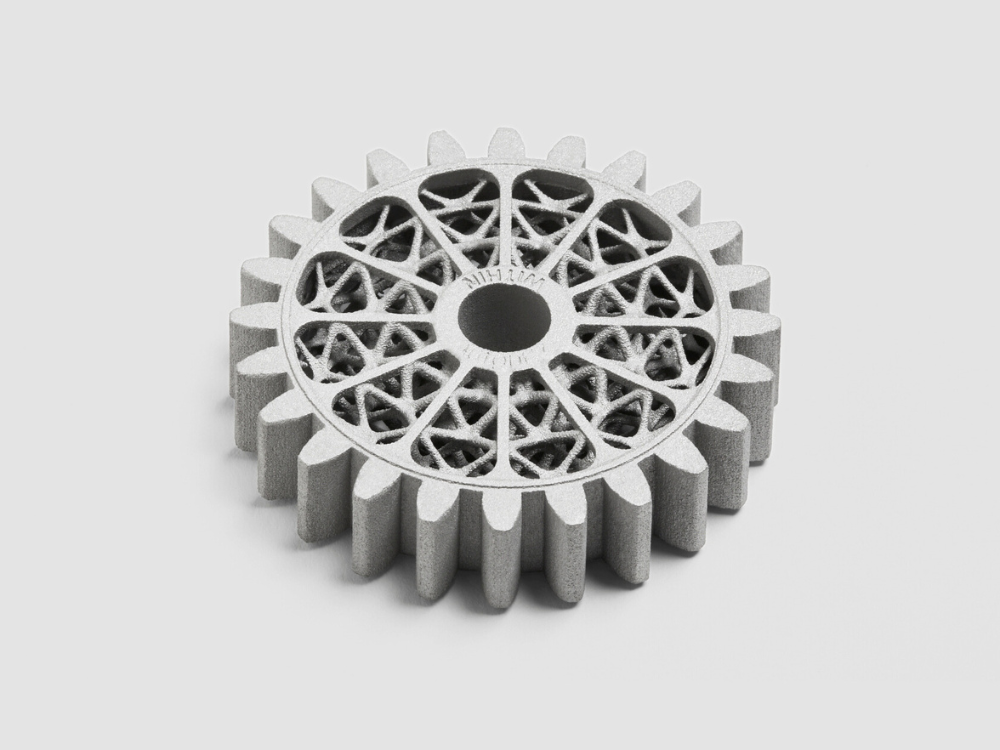
Speed and Scalability: Compared to traditional methods, metal binder jetting can produce parts faster, with the added benefit of scalability. Manufacturers can quickly transition from prototype to low- and medium-volume production.
Metal Jet Capabilities

Build Platform Volume

Build Speed
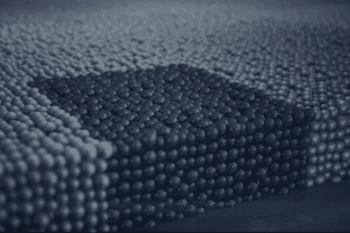
Layer Thickness
The Future of Metal Binder Jetting
As research and development continue to improve metal binder jetting technologies, we can expect to see even greater advancements in material properties, printing speeds, and part accuracy. Companies are also exploring hybrid solutions, combining binder jetting with other manufacturing techniques to enhance part performance and reduce costs.
In the coming years, we may witness a shift in the manufacturing landscape, as industries adopt metal binder jetting for more applications—from custom medical implants and aerospace components to automotive parts and tooling.

